Metabolic Bone Disease Radiology
Metabolic bone disease radiology. 6674273 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. Burnstein MI Kottamasu SR Pettifor JM Sochett E Ellis BI Frame B. Key Features Includes all imaging modalities relevant to rheumatic disease and applications and contraindications of.
It is the primary site for the effect of. Radiology of metabolic bone disease. Metabolic bone diseases are a diverse group of diseases that result in abnormalities of a bone mass b structure mineral homeostasis c bone turnover d growth.
For patients affected by these processes radiologic imaging plays a central role. The group includes osteoporosis osteomalacia hypophosphatasia renal osteodystrophy parathyroid and thyroid hormone disorders and scurvy. It represents the site where longitudinal bone growth occurs.
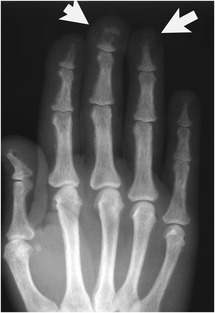
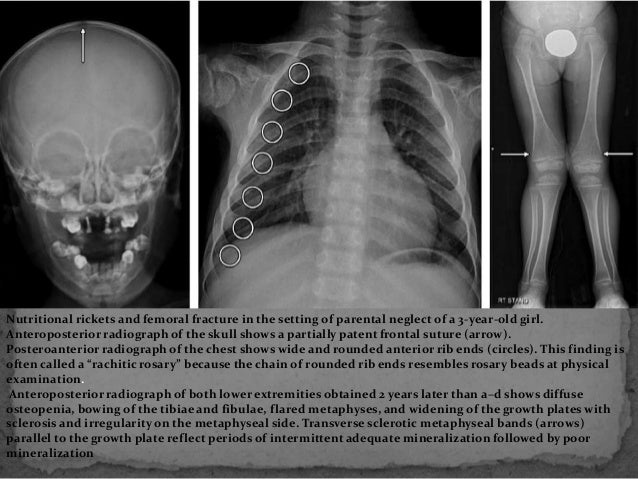
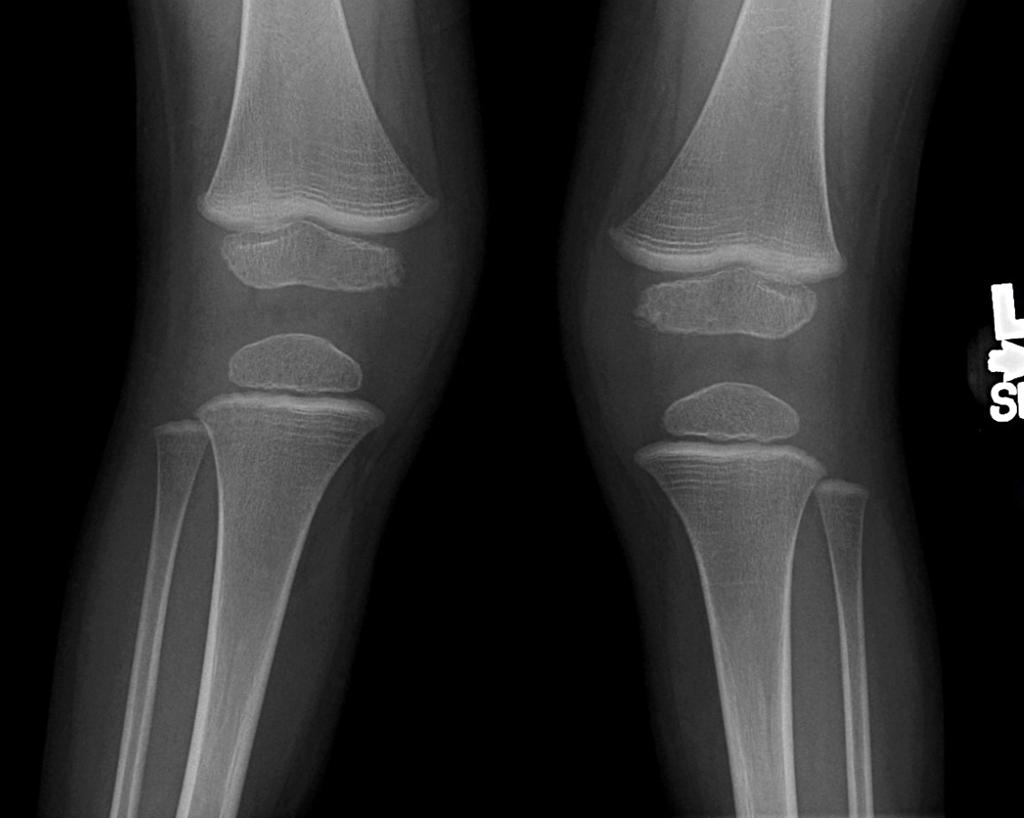
Measurement of the bone mineral content in the axial skeleton can be done by one of several methods that use CT to assess the bone quantity in the spine. Metabolic bone disease encompasses a broad spectrum of inherited and acquired disorders that disrupt the normal homeostasis of bone formation and resorption. With rickets the radiographic abnormalities are most noticeable at the anterior costochondral junctions of the middle ribs and the metaphyses around the shoulder wrist knee and ankle joints.
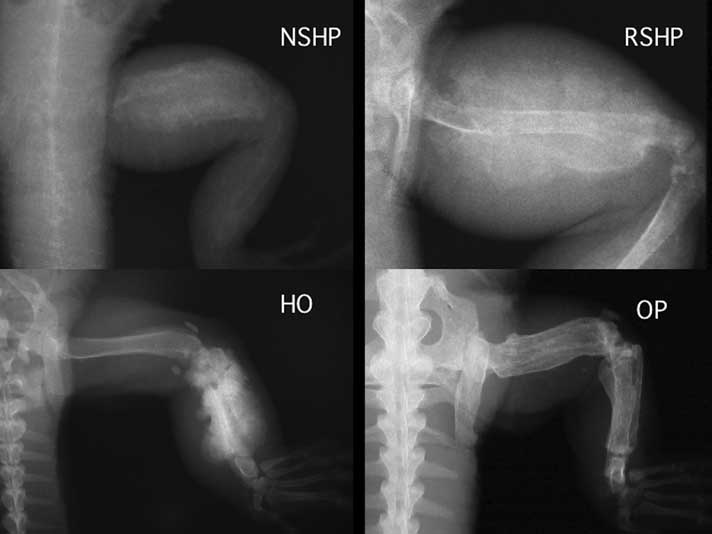
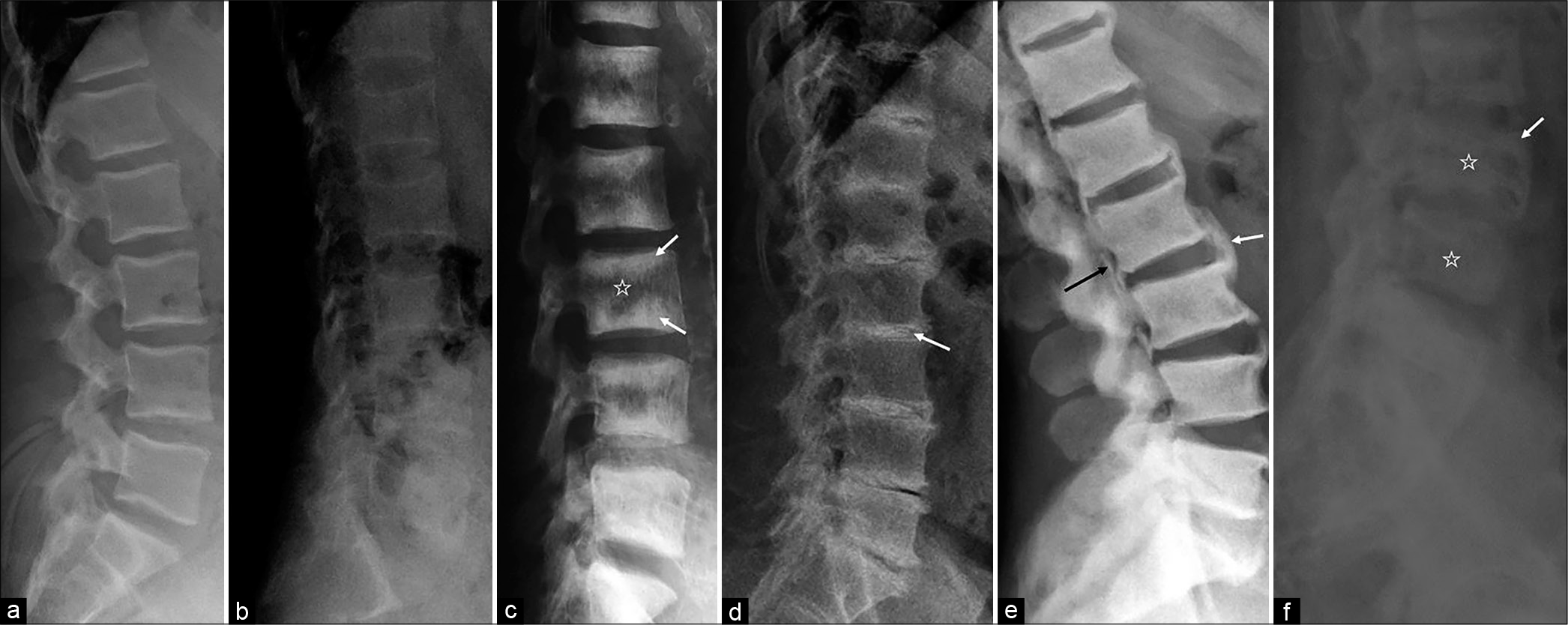
Metabolic bone disease in pseudohypoparathyroidism. Osteoporosis the most common metabolic bone disease results in generalized loss of bone mass and deterioration in the bone microarchitecture. This superb new publication puts you at the forefront of imaging in arthritis and metabolic bone disease a must have reference for the clinician and imaging specialist.
Metabolic bone diseases are a diverse group of diseases that result in abnormalities of a bone mass b structure mineral homeostasis c bone turnover or d growth. Metabolic bone diseases are a diverse group of. Metabolic bone disease encompasses a broad spectrum of inherited and acquired disorders that disrupt the normal homeostasis of bone formation and resorption.
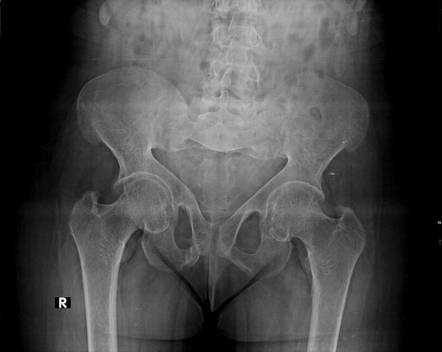
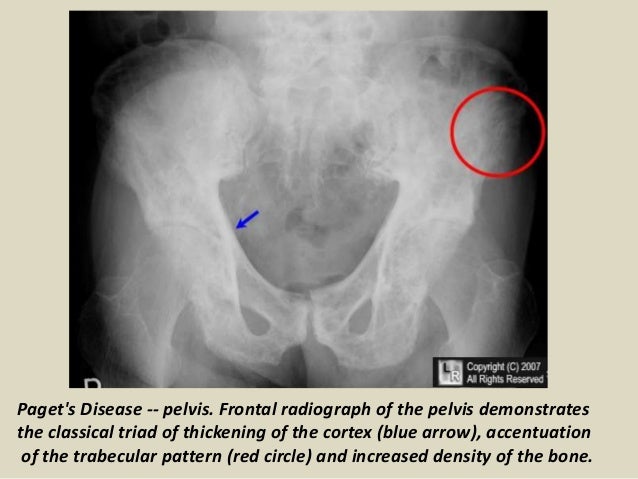
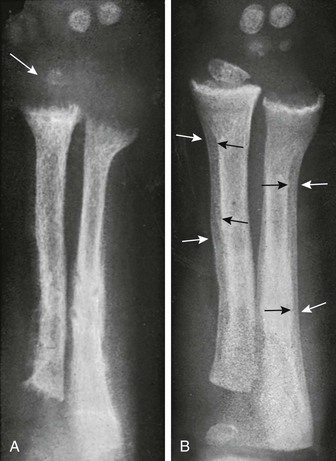
These findings though often subtle are often diagnostic. Pseudofractures Loosers zones are a radiological sign of osteomalacia The main features of Pagets disease are bone expansion and coarsening of the trabecular pattern Neuropathic arthropathyCharcot disease most commonly affects the foot in diabetics Osteoporosis is the most common metabolic disease of bone - see previous page.
Pseudofractures Loosers zones are a radiological sign of osteomalacia The main features of Pagets disease are bone expansion and coarsening of the trabecular pattern Neuropathic arthropathyCharcot disease most commonly affects the foot in diabetics Osteoporosis is the most common metabolic disease of bone - see previous page.
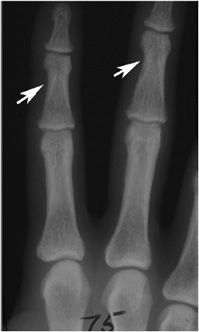
Key Features Includes all imaging modalities relevant to rheumatic disease and applications and contraindications of. Osteoporosis is defined as a condition characterized by diminished. Widening cupping and fraying of the metaphyses. Cirrhotic patients have increased risk factors for developing osteoporosis such as hypogonadism alcohol and steroid use vitamin D deficiency. Metabolic bone diseases are a diverse group of diseases that result in abnormalities of bone mass structure mineral homeostasis bone turnover or growth. The group includes osteoporosis osteomalacia hypophosphatasia renal osteodystrophy parathyroid and thyroid hormone disorders and scurvy. It represents the site where longitudinal bone growth occurs. With rickets the radiographic abnormalities are most noticeable at the anterior costochondral junctions of the middle ribs and the metaphyses around the shoulder wrist knee and ankle joints. It appears radiologically as a lucency between the epiphysis and the metaphysis.
It appears radiologically as a lucency between the epiphysis and the metaphysis. Bone Diseases Metabolicdiagnostic imaging Child Preschool. Metabolic bone diseases are a diverse group of diseases that result in abnormalities of a bone mass b structure mineral homeostasis c bone turnover or d growth. Such disorders include but are not limited to endocrine dysfunctions Paget disease and osteoporosis. Metabolic bone disease in pseudohypoparathyroidism. Pseudofractures Loosers zones are a radiological sign of osteomalacia The main features of Pagets disease are bone expansion and coarsening of the trabecular pattern Neuropathic arthropathyCharcot disease most commonly affects the foot in diabetics Osteoporosis is the most common metabolic disease of bone - see previous page. The purpose of this article is to review the radiographic findings of numerous metabolic bone diseases including osteoporosis rickets and osteomalacia hypophosphatasia hyperparathyroidism renal osteodystrophy hypoparathyroidism hypothyroidism hyperthyroidism acromegaly and scurvy.































Posting Komentar untuk "Metabolic Bone Disease Radiology"